Recently, Professor Yu Jianguo, Associate Professor Li Sen, et al., of the National Research Center for Salt Lake Resource Comprehensive Utilization Engineering Technology of our university, made important progress in the field of low-grade and high-magnesium-lithium-ratio salt lake brine lithium resource absorption and extraction, and relevant research achievements were successively published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition and AIChE Journal.
Developing efficient salt lake lithium extraction technology is significant for the sustainable supply of lithium resources. Based on the feature of the only one aluminum-based lithium adsorbent applied to the salt lake industry, the research team put forward a framework that integrated high-flux experiments and explainable machine learning technology (ML), completed quick screening of the reinforcement and modification plan, avoided the large workload brought by the traditional trial-and-error method, and generally improved the absorption volume in salt lake brines with varying characteristics by about 40%. Relevant research work was published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition and titled as Machine Learning-accelerated Design of High-efficient Lithium Adsorbents for Salt Lake Brines. The doctoral student Zhang Rui and the postgraduate Liu Siying were the first authors of the paper, and Professor Lian Cheng and Associate Professor Lin Sen of the National Salt Lake Center were both corresponding authors of the paper.
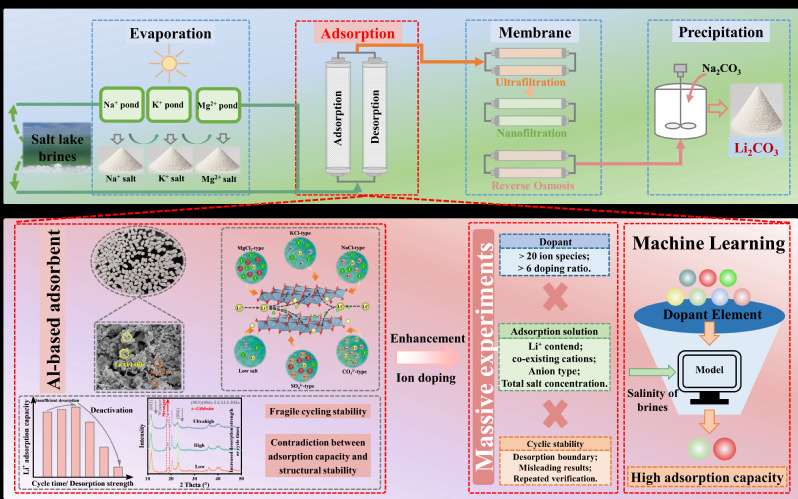
In addition, the research team, facing the problem of the low efficiency of formed granule absorption and mass transfer of the industrial aluminum-based lithium adsorbent, developed the technology of high-strength hydrophilic phase-reversal heterozygosis for forming and granulation, established a correlation quantitative model among the size of the adsorbent's granules, mass transfer kinetics, and lithium extraction performance, conducted targeted design optimization of the internal structure of granules, prepared low-dimensional forming granules with quick ion transmission channels and high-density lithium absorption sites. The adsorbent's granule abrasion resistance was improved by over 50%, and the time for quick absorption was shortened from 5.5 hours to no more than 1 hour. Related research work was published in the AIChE Journal and titled as Reduction in Adsorbent Granule Dimensionality to Strengthen Lithium Adsorption in Low-grade Salt Lakes. The postdoctoral researcher Chen Jun was the first author, and Associate Professor Lin Sen was the corresponding author of the paper.
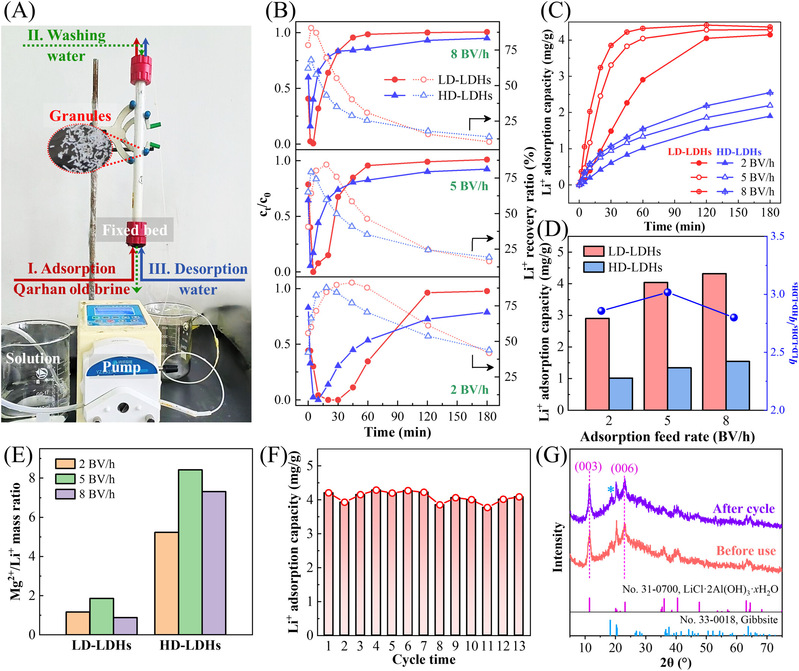
The above research tasks were finished under the thoughtful guidance of Professor Yu Jianguo of the National Research Center for Salt Lake Resource Comprehensive Utilization Engineering Technology, and Professor Lian Cheng offered help to the theoretical calculation of the research. The project's research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, etc.
Link to the original article: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202503644
https://aiche.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/aic.18795




